Do You Like To Sleep At Night? by Mike Clinger, Senior Systems Engineer
For years RAID 5 has been the choice of SAN administrators who were looking for a high capacity fault tolerant RAID solution. RAID 5 does provide a high capacity storage solution with its N-1 capacity formula. This is a very attractive offering when storage capacity is your main focus when choosing a RAID type configuration. RAID 5 is also a fault tolerant RAID configuration with its single parity hard drive and this has given SAN administrators a sense that their data is safe even if a hard drive fails. A SAN administrator would even have a greater sense of safety for their data when a hot spare was setup in their SAN array. The online hot spare would start a rebuild operation as soon as the SAN array has detected that a hard drive failure has occurred within the RAID 5 set.
It is during this rebuild process that the SAN administrator’s data is at its most vulnerable state. With today’s hard drives becoming increasingly larger in RAID 5 data sets, the rebuild times are taking longer and longer to complete - at times even taking several days to complete. During the rebuild process the RAID 5 set has no fault tolerance and if a second hard drive fails during this process the data would be lost without any fault tolerance being present. That would cause me to suffer through some restless nights of sleep while the RAID 5 set was being rebuilt.
This is why RAID 6 with a hot spare is a much better high availability RAID configuration when compared to a RAID 5 configuration with a hot spare. RAID 6 can withstand a double hard drive failure because RAID 6 uses two hard drives for parity, so this gives the SAN administrator a higher level of comfort as when compared to the RAID 5 configuration. And if a RAID 6 data set does suffer a hard drive failure, a rebuild process is initiated with a hot spare. The array is not left in a vulnerable state during the rebuild process the RAID 6 data set can still withstand a hard drive failure during the rebuild cycle. It could also keep the data intact due to the two parity drives in use by the RAID 6 configuration.
Sure Raid 6 does use an additional hard drive resource with its N-2 storage capacity formula, which does reduce storage capacity by the total size of one additional hard drive as when compared to the RAID 5 configuration. The performance is comparable to the RAID 5 configuration but the higher availability of the RAID 6 data set more than makes up for a little less capacity.
So if you like to sleep at night even when your SAN array has encountered a hard drive failure make RAID 6 your choice for a high capacity and fault tolerant RAID configuration.
About the author:
Mike Clinger has over thirty years of experience working in the information technology field. As a Senior Systems Engineer at Managed Solution, Mike contributes his strong technical expertise for projects focusing on storage, cloud and virtualization solutions.
Articles by Mike Clinger:
Continued Reading
July 5, 2015
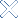
Bringing the Internet out of the clouds: exploring the datacenters that power our world
The cloud isn’t some nebulous construct that floats above us […]
LEARN MORECloud Services Page

July 6, 2015
Case Study Video: US FDA Brings Scale, and Cost Effective Innovation to New Programs Utilizing AWS Cloud
About the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) The US […]
LEARN MORECase Studies